ประโยคย่อย (Dependent Clause) เป็นส่วนสำคัญในโครงสร้างไวยากรณ์ของประโยค อย่างไรก็ตาม นักเรียนหลายคนมักสับสนระหว่าง ประโยคย่อย และ ประโยคอิสระ เมื่อสร้าง Compound-Complex Sentence บทความนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจความแตกต่างและการใช้ Dependent Clause อย่างถูกต้อง พร้อมเรียนรู้วิธีสร้างประโยคซ้อนในภาษาอังกฤษ
I. ประโยคย่อยคืออะไร
ประโยคย่อย (Dependent Clause) หรือที่เรียกว่า Subordinate Clause เป็นส่วนของประโยคที่ไม่สามารถอยู่ได้อย่างอิสระ ต้องใช้ร่วมกับ ประโยคอิสระ (Independent Clause) เพื่อสร้างประโยคที่สมบูรณ์และสื่อความหมาย
Dependent Clause ไม่สามารถอยู่ลำพังได้เพราะขาดข้อมูลสำคัญในการสื่อความหมายเมื่อ Dependent Clause รวมกับ Independent Clause จะสร้าง Complex Sentence
ตัวอย่าง:
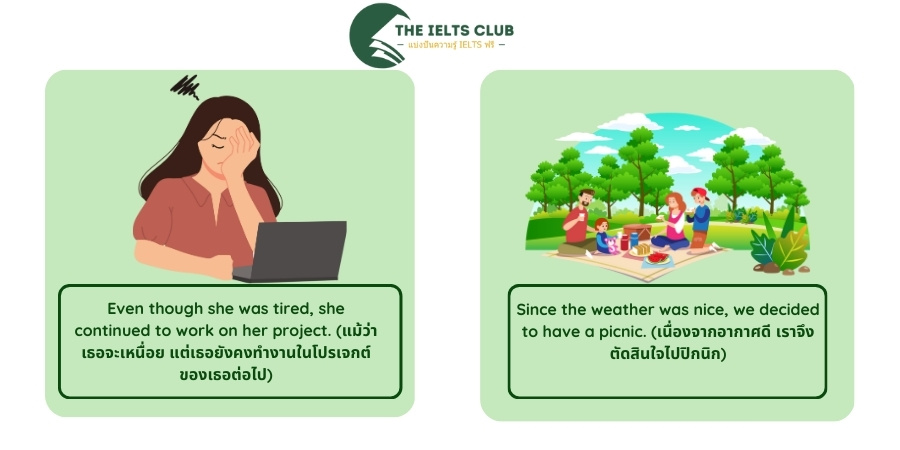
- Even though she was tired, she continued to work on her project. (แม้ว่าเธอจะเหนื่อย แต่เธอยังคงทำงานในโปรเจกต์ของเธอต่อไป)
- Dependent Clause: Even though she was tired
- Independent Clause: She continued to work on her project
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Dependent Clause บอกเงื่อนไข (เธอเหนื่อย) ส่วน Independent Clause บอกการกระทำ (ยังคงทำงานต่อ)
- Since the weather was nice, we decided to have a picnic. (เนื่องจากอากาศดี เราจึงตัดสินใจไปปิกนิก)
- Dependent Clause: Since the weather was nice
- Independent Clause: We decided to have a picnic
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Dependent Clause บอกเหตุผล ส่วน Independent Clause บอกการตัดสินใจ
II. ประเภทของประโยคย่อย (Dependent Clauses) ในภาษาอังกฤษ
1. ประโยคย่อยแบบ Noun Clause
Noun Clause คือประโยคย่อยที่ทำหน้าที่แทนคำนามในประโยค Noun Clause มักเริ่มต้นด้วยคำเชื่อมเช่น that, how, who, whoever, whom, whomever, whose, what, whatever, which, whichever, where, when, why, whether หรือ if
ตัวอย่าง:
- I believe that hard work leads to success.
- (ฉันเชื่อว่าการทำงานหนักนำไปสู่ความสำเร็จ)
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Noun Clause คือ “that hard work leads to success” ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของคำกริยา believe
- Emily knows where she wants to travel.
- (เอมิลี่รู้ว่าเธอต้องการเดินทางไปที่ไหน)
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Noun Clause คือ “where she wants to travel” ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของคำกริยา knows
2. ประโยคย่อยแบบ Adjective Clause
Adjective Clause ทำหน้าที่ขยายความหรืออธิบายคำนามหรือสรรพนามในประโยคหลัก มักเริ่มต้นด้วยคำเชื่อมเช่น who, whom, whose, which, that หรือคำเชื่อมที่เป็น Relative Adverbs เช่น when, why, where
ตัวอย่าง:
- I have a friend who loves photography.
- (ฉันมีเพื่อนที่รักการถ่ายภาพ)
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Adjective Clause คือ “who loves photography” ทำหน้าที่อธิบายคำนาม friend
- The car that he bought last year is very expensive.
- (รถที่เขาซื้อเมื่อปีที่แล้วมีราคาสูงมาก)
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Adjective Clause คือ “that he bought last year” ทำหน้าที่ขยายคำนาม car
3. ประโยคย่อยแบบ Adverbial Clause
Adverbial Clause ทำหน้าที่เหมือนกริยาวิเศษณ์ในประโยค โดยให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับเวลา สถานที่ เหตุผล จุดประสงค์ เงื่อนไข หรือวิธีการของการกระทำ มักเริ่มต้นด้วยคำเชื่อม เช่น
- เวลา: When, While, As, Until
- การยอมรับ: Although, Though, Even though
- จุดประสงค์: So that, In order to, In order that
- เหตุผล: Because, As, Since
ตัวอย่าง:
- He left early because he had an appointment.
- (เขาออกไปแต่เช้าเพราะเขามีนัด)
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Adverbial Clause คือ “because he had an appointment” ทำหน้าที่อธิบายเหตุผลของการกระทำ
- Sarah studied hard so that she could pass the test.
- (ซาร่าตั้งใจเรียนเพื่อที่เธอจะสอบผ่าน)
- ในตัวอย่างนี้ Adverbial Clause คือ “so that she could pass the test” ทำหน้าที่อธิบายจุดประสงค์
III. วิธีสร้างประโยคซ้อนจากประโยคอิสระและประโยคย่อย
การสร้าง Complex Sentence เกิดจากการเชื่อม ประโยคอิสระ (Independent Clause) และ ประโยคย่อย (Dependent Clause) เข้าด้วยกันโดยใช้คำเชื่อม Subordinating Conjunctions (เช่น when, while, because, although, since, unless เป็นต้น) หรือ Relative Pronouns (เช่น who, whom, which, that เป็นต้น)
ประโยคอิสระ สามารถอยู่ได้อย่างอิสระและมีความหมายสมบูรณ์ ในขณะที่ ประโยคย่อย จำเป็นต้องพึ่งพาประโยคอื่นเพื่อให้มีความหมายสมบูรณ์
โครงสร้างทั่วไป:
- Dependent Clause (ประโยคอิสระ) + Independent Clause (ประโยคย่อย)
คุณสามารถสร้างประโยคซ้อนแบบง่าย ๆ ด้วย 1 ประโยคอิสระ และ 1 ประโยคย่อย หรือสร้างประโยคซ้อนที่ซับซ้อนยิ่งขึ้นด้วย 1 ประโยคอิสระ และ หลายประโยคย่อย
ตัวอย่าง:
- Even though the weather was cold, they went hiking in the mountains. (แม้ว่าสภาพอากาศจะหนาว แต่พวกเขาก็ไปเดินป่าบนภูเขา)
- Dependent Clause: Even though the weather was cold
- Independent Clause: They went hiking in the mountains
- คำอธิบาย: ประโยคย่อยแสดงเงื่อนไข (อากาศหนาว) และประโยคอิสระแสดงการกระทำ (ไปเดินป่า)
- Jack worked late into the night because he had a deadline to meet. (แจ็คทำงานจนดึกเพราะเขามีเส้นตายที่ต้องทำให้เสร็จ)
- Independent Clause: Jack worked late into the night
- Dependent Clause: Because he had a deadline to meet
- คำอธิบาย: ประโยคย่อยให้เหตุผล (มีเส้นตาย) และประโยคอิสระแสดงการกระทำ (ทำงานจนดึก)
- Liam decided to stay home, although his friends invited him to the party. (เลียมตัดสินใจอยู่บ้าน แม้ว่าจะมีเพื่อนชวนไปงานเลี้ยง)
- Independent Clause: Liam decided to stay home
- Dependent Clause: Although his friends invited him to the party
- คำอธิบาย: ประโยคย่อยแสดงเงื่อนไข (เพื่อนชวนไปงานเลี้ยง) และประโยคอิสระแสดงการตัดสินใจ (อยู่บ้าน)
- Emma enjoys reading novels, but she finds poetry difficult to understand because of its abstract nature. (เอ็มม่าชอบอ่านนวนิยาย แต่เธอพบว่าบทกวีเข้าใจยากเพราะมีความเป็นนามธรรม)
- Independent Clause: Emma enjoys reading novels
- Dependent Clause 1: She finds poetry difficult to understand
- Dependent Clause 2: Because of its abstract nature
- คำอธิบาย: ประโยคซ้อนนี้มีประโยคอิสระและ 2 ประโยคย่อยที่อธิบายการกระทำและเหตุผล
IV. แบบฝึกหัดประโยคย่อย (Dependent Clause) ในภาษาอังกฤษ
ลองฝึกฝนแบบฝึกหัดด้านล่างเพื่อให้คุณเข้าใจและใช้งาน Dependent Clause ในภาษาอังกฤษได้อย่างถูกต้อง
แบบฝึกหัด:
ระบุประโยคย่อยในประโยคต่อไปนี้
- I stayed up late because I needed to finish my project.
- She smiled when she heard the good news.
- Although the traffic was heavy, we managed to arrive on time.
- He won’t go outside until the rain stops.
- Sarah decided to stay home since she wasn’t feeling well.
- Even though the test was difficult, he scored very high.
- I’ll call you after I complete my meeting.
- Unless you arrive early, you might miss the presentation.
- Before she left, she double-checked her luggage.
- If you need help, just let me know.
เฉลย:
- Dependent Clause: because I needed to finish my project
- Dependent Clause: when she heard the good news
- Dependent Clause: Although the traffic was heavy
- Dependent Clause: until the rain stops
- Dependent Clause: since she wasn’t feeling well
- Dependent Clause: Even though the test was difficult
- Dependent Clause: after I complete my meeting
- Dependent Clause: Unless you arrive early
- Dependent Clause: Before she left
- Dependent Clause: If you need help
Dependent Clause เป็นส่วนสำคัญของไวยากรณ์ภาษาอังกฤษ การฝึกระบุและใช้ประโยคย่อยร่วมกับประโยคอิสระช่วยให้คุณสร้างประโยคที่ซับซ้อนและน่าสนใจมากขึ้น อย่าลืมฝึกฝนอย่างต่อเนื่องเพื่อพัฒนาทักษะของคุณ!